
This menu is not available on the FL MGUARD BLADE controller. A reduced version of the menu is available on the FL MGUARD RS2000 , TC MGUARD RS2000 3G , TC MGUARD RS2000 4G , and FL MGUARD RS2005 .
This menu is not available on the FL MGUARD BLADE controller. A reduced version of the menu is available on the FL MGUARD RS2000 , TC MGUARD RS2000 3G , TC MGUARD RS2000 4G , and FL MGUARD RS2005 . |
8.1Network Security >> Packet Filter
The mGuard includes a Stateful Packet Inspection Firewall. The connection data of an active connection is recorded in a database (connection tracking). Rules therefore only have to be defined for one direction. This means that data from the other direction of the relevant connection, and only this data, is automatically allowed through.
A side effect is that existing connections are not aborted during reconfiguration, even if a corresponding new connection can no longer be established.
The firewall rules configured under Network security >> Packet filter are not used on IP packets which are directed to an mGuard IP address. They only apply to IP connections or IP traffic which passes through the mGuard .
–All incoming connections are discarded (excluding VPN).
–Data packets of all outgoing connections are allowed through.
The firewall rules here have an effect on the firewall that is permanently active, with the exception of:
–VPN connections. Individual firewall rules are defined for VPN connections (see "IPsec VPN >> Connections" on page 320, "Firewall" on page 349).
–User firewall. When a user logs in, for whom user firewall rules are defined, these rules take priority (see "Network Security >> User Firewall" on page 290), followed by the permanently active firewall rules.
If multiple firewall rules are defined, these are queried starting from the top of the list of entries until an appropriate rule is found. This rule is then applied. If the list of rules contains further subsequent rules that could also apply, these rules are ignored. |
Firewall settings for devices from the RS2000 series
FL MGUARD RS2000 , TC MGUARD RS2000 3G , TC MGUARD RS2000 4G and FL MGUARD RS2005 have a simple firewall functionality. The following functions are not supported: –Firewall rule sets cannot be configured. –MAC filters cannot be configured. –A user firewall cannot be configured. –Host names in IP-groups cannot be used.
Caution: configuration profiles which include the corresponding settings cannot be imported. |
Use of host names in IP groups (firewall rules)
Host names can also be specified in IP groups in addition to IP addresses, IP areas, and networks (DNS-based firewall rules). IP address resolution of host names is performed according to the DNS settings of the mGuard . This allows host names to be used in firewall groups via IP groups (see "IP/Port Groups" on page 276).
NOTE: When using host names, there is always the risk of an attacker manipulating or blocking DNS requests (i.e. DNS spoofing). You should therefore only configure trustworthy and secure DNS servers from your internal company network on the mGuard , so as to avoid these types of attacks. For security reasons, IP groups that contain host names should not be used in firewall rules which execute “Drop” or “Reject” as the action. |
If a host name from an IP group cannot be resolved, e.g., because a DNS server has not been configured or cannot be reached, this host will not be taken into consideration for the rule. Further entries in the IP group are not affected by this and are taken into consideration. |
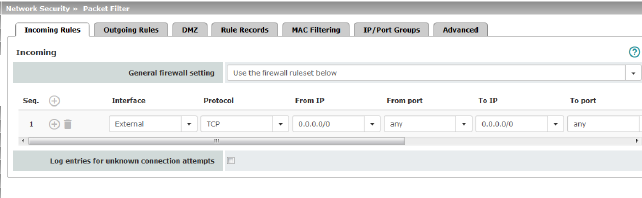
Lists the firewall rules that have been set up. They apply for incoming data links that have been initiated externally. Special firewall settings apply for the mGuard devices from the RS2000 series (see "Firewall settings for devices from the RS2000 series" on page 259). All incoming connections are discarded (excluding VPN) in the default setting. 

|
||
|
General firewall setting |
Accept all connections: the data packets of all incoming connections are allowed. Drop all connections: the data packets of all incoming connections are discarded. Accept Ping only: the data packets of all incoming connections are discarded, except for ping packets (ICMP). This setting allows all ping packets to pass through. The integrated protection against brute force attacks is not effective in this case. Use the firewall ruleset below: displays further setting options. |
|
The following settings are only visible if “Use the firewall ruleset below” is set. |
|
|
Interface |
External / External 2 / Any Specifies via which interface the data packets are received so that the rule applies to them. Any refers to the External and External 2 interfaces. These interfaces are only available on mGuard models that have a serial interface with external access. |
|
Protocol |
All means TCP, UDP, ICMP, GRE, and other IP protocols |
|
From IP / To IP |
0.0.0.0/0 means all IP addresses. To specify an address area, use CIDR format (see "CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing)" on page 29). Name of IP groups, if defined. When a name is specified for an IP group, the host names, IP addresses, IP areas or networks saved under this name are taken into consideration (see IP/Port Groups tab page). 

|
|
(Only for TCP and UDP protocols) |
any refers to any port. startport:endport (e.g., 110:120) refers to a port range. Individual ports can be specified using the port number or the corresponding service name (e.g., 110 for pop3 or pop3 for 110). Name of port groups, if defined. When a name is specified for a port group, the ports or port ranges saved under this name are taken into consideration (see IP/Port Groups tab page). |
|
Action |
Accept means that the data packets may pass through. Reject means that the data packets are sent back and the sender is informed of their rejection. 
Drop means that the data packets are not permitted to pass through. They are discarded, which means that the sender is not informed of their whereabouts. Name of rule sets, if defined. When a rule set is selected, the firewall rules configured under this rule set take effect (see "Rule Records" on page 270). 

Name of Modbus TCP rule sets, if defined. When a Modbus TCP rule set is selected, the firewall rules configured under this rule set take effect (see "Modbus TCP" on page 283). |
|
Freely selectable comment for this rule. |
|
|
Log |
For each individual firewall rule, you can specify whether the use of the rule: –Should be logged – activate Log function –Should not be logged – deactivate Log function (default) |
|
Log entries for unknown connection attempts |
When the function is activated, all connection attempts that are not covered by the rules defined above are logged. (Default setting: deactivated) |
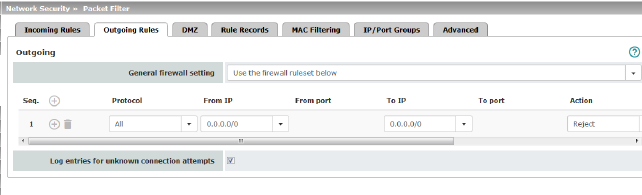
Outgoing |
Lists the firewall rules that have been set up. They apply for outgoing data links that have been initiated internally in order to communicate with a remote peer. Special firewall settings apply for the mGuard devices from the RS2000 series (see "Firewall settings for devices from the RS2000 series" on page 259). A rule is defined by default that allows all outgoing connections. 
|
|
|
General firewall setting |
Accept all connections: the data packets of all outgoing connections are allowed. Drop all connections: the data packets of all outgoing connections are discarded. Accept Ping only: the data packets of all outgoing connections are discarded, except for ping packets (ICMP). Use the firewall ruleset below: displays further setting options. |
|
The following settings are only visible if “Use the firewall ruleset below” is set. |
|
|
Protocol |
All means TCP, UDP, ICMP, GRE, and other IP protocols |
|
From IP / To IP |
0.0.0.0/0 means all IP addresses. To specify an address area, use CIDR format (see "CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing)" on page 29). Name of IP groups, if defined. When a name is specified for an IP group, the host names, IP addresses, IP areas or networks saved under this name are taken into consideration (see IP/Port Groups tab page). 

|
|
From port / To port (Only for TCP and UDP protocols) |
any refers to any port. startport:endport (e.g., 110:120) refers to a port range. Individual ports can be specified using the port number or the corresponding service name (e.g., 110 for pop3 or pop3 for 110). Name of port groups, if defined. When a name is specified for a port group, the ports or port ranges saved under this name are taken into consideration (see IP/Port Groups tab page). |
|
Action |
Accept means that the data packets may pass through. Reject means that the data packets are sent back and the sender is informed of their rejection. 
. Drop means that the data packets are not permitted to pass through. They are discarded, which means that the sender is not informed of their whereabouts. Name of rule sets, if defined. When a rule set is selected, the firewall rules configured under this rule set take effect (see "Rule Records" on page 270). 

Name of Modbus TCP rule sets, if defined. When a Modbus TCP rule set is selected, the firewall rules configured under this rule set take effect (see "Modbus TCP" on page 283). |
|
Comment |
Freely selectable comment for this firewall rule. |
|
Log |
For each individual firewall rule, you can specify whether the use of the rule: –Should be logged – activate Log action –Should not be logged – deactivate Log action (default) |
|
Log entries for unknown connection attempts |
When the function is activated, all connection attempts that are not covered by the rules defined above are logged. (Default setting: deactivated) |
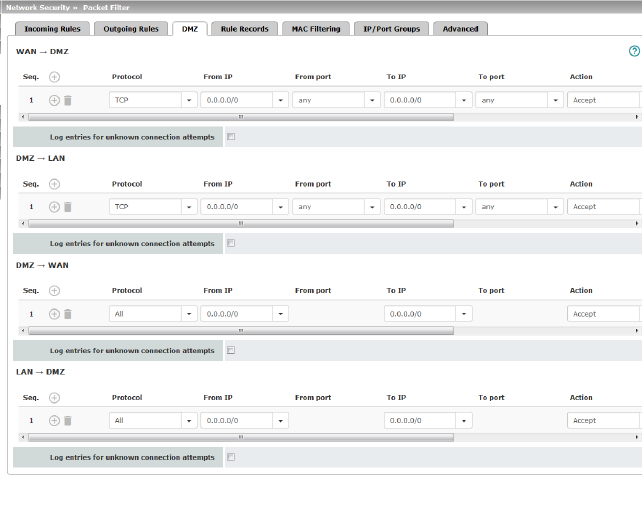
Firewall rules for the DMZ (Only for TC MGUARD RS4000 3G , TC MGUARD RS4000 4G , FL MGUARD RS4004 , FL MGUARD CENTERPORT ) |
The DMZ can be protected against attacks from the internal network (LAN interface) and the external network (WAN interface) using a dedicated set of firewall rules. The settings are split into four possible directions of network traffic. |
|
WAN DMZ |
|
If no rule has
been set, the data packets of all incoming connections (excluding
VPN) are dropped |
DMZ LAN |
|
If no rule has
been set, the data packets of all outgoing connections (excluding
VPN) are dropped |
DMZ WAN |
|
A rule is defined by default that allows all outgoing connections. |
LAN DMZ |
|
A rule is defined by default that allows all incoming connections. |
|
Protocol |
All means TCP, UDP, ICMP, GRE, and other IP protocols |
|
From IP / To IP |
0.0.0.0/0 means all IP addresses. To specify an address area, use CIDR format (see "CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing)" on page 29). Name of IP groups, if defined. When a name is specified for an IP group, the host names, IP addresses, IP areas or networks saved under this name are taken into consideration (see IP/Port Groups tab page). 
|
|
From port / To port (Only for TCP and UDP protocols) |
any refers to any port. startport:endport (e.g., 110:120) refers to a port range. Individual ports can be specified using the port number or the corresponding service name (e.g., 110 for pop3 or pop3 for 110). Name of port groups, if defined. When a name is specified for a port group, the ports or port ranges saved under this name are taken into consideration (see IP/Port Groups tab page). |
|
Action |
Accept means that the data packets may pass through. Reject means that the data packets are sent back and the sender is informed of their rejection. 
. Drop means that the data packets are not permitted to pass through. They are discarded, which means that the sender is not informed of their whereabouts. Name of rule sets, if defined. When a rule set is selected, the firewall rules configured under this rule set take effect (see "Rule Records" on page 270). 
Name of Modbus TCP rule sets, if defined. When a Modbus TCP rule set is selected, the firewall rules configured under this rule set take effect (see "Modbus TCP" on page 283). |
|
Comment |
Freely selectable comment for this rule. |
|
Log |
For each individual firewall rule, you can specify whether the use of the rule: –Should be logged – activate Log action –Should not be logged – deactivate Log action (default) |
|
Log entries for unknown connection attempts |
When the function is activated, all connection attempts that are not covered by the rules defined above are logged. (Default setting: deactivated) |
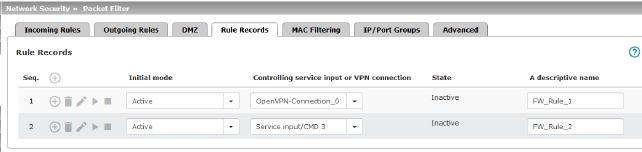
Rule Records (This menu item is not included in the scope of functions for TC MGUARD RS2000 3G , TC MGUARD RS2000 4G , FL MGUARD RS2005 or FL MGUARD RS2000 .) |
Initial mode |
Disabled / Active / Inactive Determines the output state of the firewall rule set following a reconfiguration or restart. The “Active/Inactive” setting is only applicable if a pushbutton is connected. If the firewall rule sets are controlled via a switch or VPN connection, they have priority. If set to “Disabled”, the firewall rule set cannot be dynamically enabled. The firewall rule set is retained but has no influence. |
|
Controlling service input or VPN connection |
Service input CMD 1-3, VPN connection The firewall rule set can be switched via a pushbutton/switch or a VPN connection. The pushbutton/switch must be connected to one of the service contacts (CMD 1-3). |
|
State |
Indicates the current state. |
|
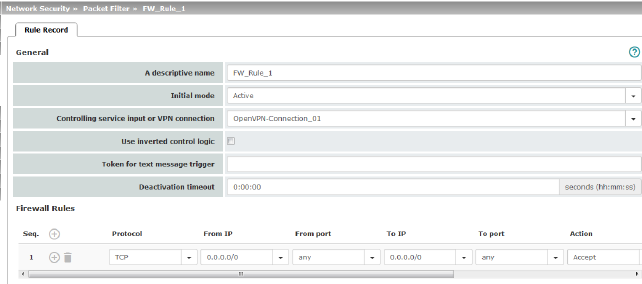
A descriptive name |
The firewall rule set can be freely named/renamed. |
|
Activate / Inactivate rule set |
Activate / Inactivate You can enable or disable the
rule set by clicking on the |
The
following tab page appears when you click on the |
||
|
||
General |
A descriptive name |
The firewall rule set can be freely named/renamed. |
|
Initial mode |
Disabled / Active / Inactive Determines the output state of the firewall rule set following a reconfiguration or restart. The “Active/Inactive” setting is only applicable if a pushbutton is connected. If the firewall rule sets are controlled via a switch or VPN connection, they have priority. If set to “Disabled”, the firewall rule set cannot be dynamically enabled. It is retained but has no influence. |
|
Controlling service input or VPN connection |
Service input CMD 1-3, VPN connection The firewall rule set can be switched via a pushbutton/switch or a VPN connection. The pushbutton/switch must be connected to one of the service contacts (CMD 1-3). |
|
Use inverted control logic |
Inverts the behavior of the connected pushbutton/switch or the controlling VPN connection. If the controlling service input is configured as an on/off switch, it can activate one firewall rule set while simultaneously deactivating another, for example. The same is true for the controlling VPN connections. |
|
Only available with the TC MGUARD RS4000 3G , TC MGUARD RS4000 4G . Incoming text messages can be used to activate or deactivate firewall rule sets. The text message must contain the “fwrules/active” or “fwrules/inactive” command followed by the token. |
|
|
Deactivation timeout |
Activated firewall rule sets are deactivated after this time has elapsed. 0 means the setting is disabled. Time in hh:mm:ss (1 day maximum) The entry can be in seconds [ss], minutes and seconds [mm:ss] or hours, minutes, and seconds [hh:mm:ss]. |
Firewall Rules |
Protocol |
All means TCP, UDP, ICMP, GRE, and other IP protocols. |
|
From IP |
0.0.0.0/0 means all IP addresses. To specify an address area, use CIDR format (see "CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing)" on page 29). Name of IP groups, if defined. When a name is specified for an IP group, the host names, IP addresses, IP areas or networks saved under this name are taken into consideration (see IP/Port Groups tab page). 
|
|
From port / To port (Only for TCP and UDP protocols) |
any refers to any port. startport:endport (e.g., 110:120) refers to a port range. Individual ports can be specified using the port number or the corresponding service name (e.g., 110 for pop3 or pop3 for 110). Name of port groups, if defined. When a name is specified for a port group, the ports or port ranges saved under this name are taken into consideration (see IP/Port Groups tab page). |
|
Action |
Accept means that the data packets may pass through. Reject means that the data packets are sent back and the sender is informed of their rejection. 
Drop means that the data packets are not permitted to pass through. They are discarded, which means that the sender is not informed of their whereabouts. Name of rule sets, if defined. When a rule set is selected, the firewall rules configured under this rule set take effect (see "Rule Records" on page 270). 
Name of Modbus TCP rule sets, if defined. When a Modbus TCP rule set is selected, the firewall rules configured under this rule set take effect (see "Modbus TCP" on page 283). |
|
Comment |
Freely selectable comment for this rule. |
|
Log |
For each firewall rule, you can specify whether the use of the rule: –Should be logged – activate Log function –Should not be logged – deactivate Log function (default) |
If a connection associated with a firewall rule set has been established and is continuously creating data traffic, deactivation of the firewall rule set might not interrupt this connection as expected. |
This happens because the (outgoing) response of a service on the LAN side creates an entry in the connection tracking table which enables a different (incoming) request from an external peer. This peer passes the firewall using the same parameters, however, it is not connected to the firewall rule set.
There are two ways to set up the mGuard so that it interrupts the associated connections when deactivating the firewall rule set.
–Activate the "Allow TCP connections upon SYN only" option under Network Security >> Packet Filter >> Advanced.
–In the firewall, block the outgoing connections that operate via the port that is the destination for the incoming connections.
If, for example, the firewall rule set enables incoming data traffic on port 22, an outgoing rule can be set up that deactivates any data traffic coming from port 22.
The incoming and outgoing rules only apply to the Network mode Stealth. |
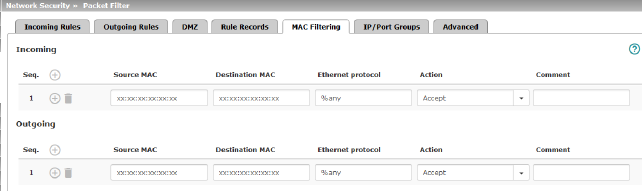
The “Incoming” MAC filter is applied to frames that the mGuard receives at the WAN interface. The “Outgoing” MAC filter is applied to frames that the mGuard receives at the LAN interface. Data packets that are received or sent via a modem connection on models with a serial interface1 are not picked up by the MAC filter because the Ethernet protocol is not used here.
In Stealth mode, in addition to the packet filter (Layer 3/4) that filters data traffic, e.g., according to ICMP messages or TCP/UDP connections, a MAC filter (Layer 2) can also be set. A MAC filter (Layer 2) filters according to MAC addresses and Ethernet protocols.
In contrast to the packet filter, the MAC
filter is stateless. If rules are introduced, corresponding rules must
also be created for the opposite direction.
If no rules are set, all ARP and IP packets are allowed to pass through.
When setting MAC filter rules, please note the information displayed on the screen. The rules defined here have priority over packet filter rules. The MAC filter does not support logging. |
Network Security >> Packet Filter >> MAC Filtering |
||
|---|---|---|
Incoming (This menu item is not included in the scope of functions for TC MGUARD RS2000 3G , TC MGUARD RS2000 4G , FL MGUARD RS2005 or FL MGUARD RS2000 .) |
Source MAC |
xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx stands for all MAC addresses. |
|
Destination MAC |
xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx stands for all MAC addresses. ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff stands for the broadcast MAC address to which all ARP requests are sent, for example. |
|
%any stands for all Ethernet protocols. Additional protocols can be specified in name or hexadecimal format, for example: –IPv4 or 0800 –ARP or 0806 |
|
|
Action |
Accept means that the data packets may pass through. Drop means that the data packets are not permitted to pass through (they are dropped). |
|
Comment |
Freely selectable comment for this rule. |
Outgoing |
The explanation provided under “Incoming” also applies to “Outgoing”. |
|
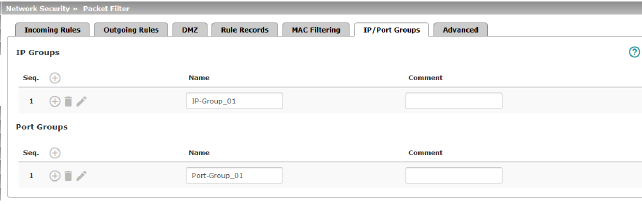
IP and port groups enable the easy creation and management of firewall and NAT rules in complex network structures.
Host names, IP addresses, IP areas, and networks can be grouped in IP groups and identified by a name. Likewise, ports or port ranges can be grouped in port groups.
If a firewall or NAT rule is created, instead of IP addresses/IP areas or ports/port ranges, the IP or port groups can be selected directly in the corresponding fields and assigned the rule.
NOTE: When using host names, there is always the risk of an attacker manipulating or blocking DNS requests (i.e. DNS spoofing). You should therefore only configure trustworthy and secure DNS servers from your internal company network on the mGuard , so as to avoid these types of attacks. For security reasons, IP groups that contain host names should not be used in firewall rules which execute “Drop” or “Reject” as the action. |
Use of hostnames Address resolution of hostnames is performed according to the DNS settings of the mGuard (see "Network >> DNS" on page 208). If a host name can be resolved in several IP addresses, all IP addresses returned by the DNS server are taken into consideration. If a host name from an IP group cannot be resolved, e.g., because a DNS server has not been configured or cannot be reached, this host will not be taken into consideration for the rule. Further entries in the IP group are not affected by this and are taken into consideration. If a DNS server resolves a resolved host name with another IP address after the TTL has elapsed, an existing connection to the original IP address is not aborted. |
mGuard devices of the RS2000 series The use of host names in IP groups is not supported by mGuard devices of the RS2000 series. |
Network Security >> Packet Filter >> IP/Port Groups |
||
|---|---|---|
IP Groups |
Name |
The IP group can be freely named/renamed. |
|
Comment |
Freely selectable comment for this group/rule. |
Edit |
The
following tab page appears when you click on the |
|
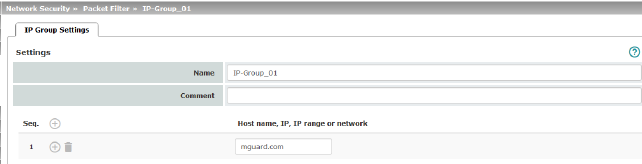
|
||
Name |
The IP group can be freely named/renamed. |
|
|
Comment |
Freely selectable comment for this group/rule. |
|
Host name, IP, IP range or network |
The entries can specify a host name (e.g., mguard.com), an IP address (e.g., 192.168.3.1), an IP address area (e.g., 192.168.3.1-192.168.3.10) or a network in CIDR format (e.g., 192.168.1.0/24). 
|
Port groups |
Name |
The port group can be freely named/renamed. |
|
Comment |
Freely selectable comment for this group/rule. |
Edit |
The
following tab page appears when you click on the |
|
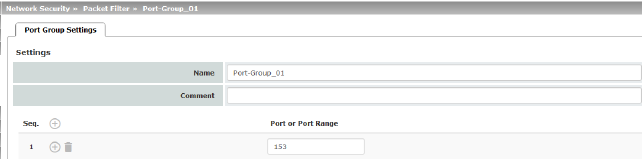
|
||
Port Group Settings |
Name |
The port group can be freely named/renamed. |
|
Comment |
Freely selectable comment for this group/rule. |
|
Port or Port Range |
The entries can specify a port (e.g., pop3 or 110) or a port range (e.g., 110:120 or 110-120). |
The following settings affect the basic behavior of the firewall.
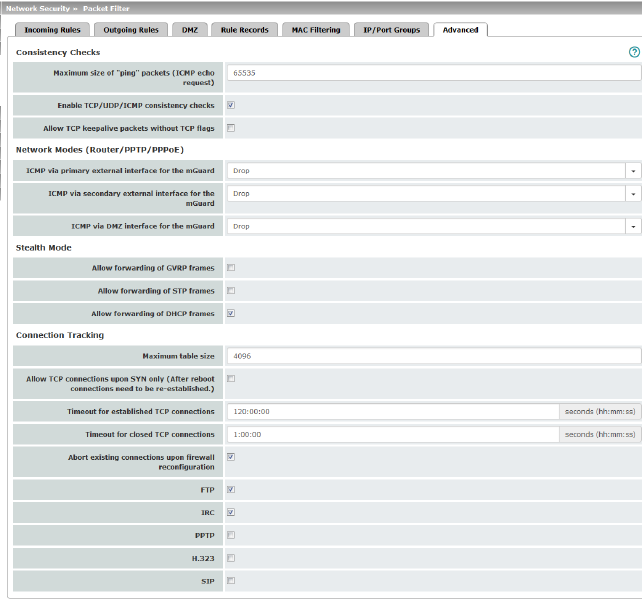
Consistency checks (This menu item is not included in the scope of functions for TC MGUARD RS2000 3G , TC MGUARD RS2000 4G , FL MGUARD RS2005 or FL MGUARD RS2000 .) |
Refers to the length of the entire packet including the header. The packet length is normally 64 bytes, but it can be larger. If oversized packets are to be blocked (to prevent bottlenecks), a maximum value can be specified. This value should be more than 64 bytes in order to not block normal ICMP echo requests. |
|
|
Enable TCP/UDP/ICMP consistency checks |
When the function is activated, the mGuard performs a range of tests to check for incorrect checksums, packet sizes, etc. and drops packets that fail these tests. The function is deactivated by default. |
|
Allow TCP keepalive packets without TCP flags |
TCP packets without flags set in their TCP header are normally rejected by firewalls. At least one type of Siemens controller with older firmware sends TCP keepalive packets without TCP flags set. These are therefore discarded as invalid by the mGuard . When the function is activated, forwarding of TCP packets where no TCP flags are set in the header is enabled. This only applies when TCP packets of this type are sent within an existing TCP connection established in the regular way. TCP packets without TCP flags do not result in a new entry in the connection table (see "Connection Tracking" on page 280). If the connection is already established when the mGuard is restarted, the corresponding packets are still rejected and connection problems can be observed as long as no packets with flags belonging to the connection are sent. These settings affect all the TCP packets without flags. Activation of this function therefore weakens the security functions provided by the mGuard . |
ICMP via primary external interface for the mGuard ICMP via secondary external interface for the mGuard ICMP via DMZ interface for the mGuard |
This option can be used to control the behavior of the mGuard when ICMP messages are received from the external network via the primary/secondary external interface. 
Drop: all ICMP messages to all IP addresses of the mGuard are dropped. Allow ping requests: only ping messages (ICMP type 8) to all IP addresses of the mGuard are accepted. Allow all ICMPs: all types of ICMP messages to all IP addresses of the mGuard are accepted. |
|
The GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) is used by GVRP-capable switches to exchange configuration information. When the function is activated, GVRP packets are allowed to pass through the mGuard in Stealth mode. |
||
|
Allow forwarding of STP frames |
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) (802.1d) is used by bridges and switches to detect and allow for loops in the cabling. When the function is activated, STP packets are allowed to pass through the mGuard in Stealth mode. |
|
Allow forwarding of DHCP frames |
When the function is activated, the client is allowed to obtain an IP address via DHCP – regardless of the firewall rules for outgoing data traffic. The function is activated by default. |
This entry specifies an upper limit. This is set to a value that can never be reached during normal practical operation. However, it can be easily reached in the event of attacks, thus providing additional protection. If there are special requirements in your operating environment, this value can be increased. Connections established from the mGuard are also counted. This value must therefore not be set too low, as this will otherwise cause malfunctions. |
||
|
SYN is a special data packet used in TCP/IP connection establishment that marks the beginning of the connection establishment process. Function deactivated (default): the mGuard also allows connections where the beginning has not been registered. This means that the mGuard can perform a restart when a connection is present without interrupting the connection. Function activated: the mGuard must have registered the SYN packet of an existing connection. Otherwise, the connection is aborted. If the mGuard performs a restart while a connection is present, this connection is interrupted. Attacks on and the hijacking of existing connections are thus prevented. |
|
|
If a TCP connection is not used during the time period specified here, the connection data is deleted. A connection translated by NAT (not 1:1 NAT) must then be reestablished. If the "Allow TCP connections upon SYN only" function has been activated, all expired connections must be reestablished. Default setting: 120 days (120:00:00) The entry can be in seconds [ss], minutes and seconds [mm:ss] or hours, minutes, and seconds [hh:mm:ss]. |
|
|
Timeout for closed TCP connections |
The timeout specifies how long the mGuard keeps a TCP-connection open when one side ends the connection with a "FIN packet", but the peer has not yet confirmed this. Default setting: 1 hour (1:00:00) The entry can be in seconds [ss], minutes and seconds [mm:ss] or hours, minutes, and seconds [hh:mm:ss]. |
|
When the function is activated (default), the existing connections are reset if the following applies: –If the "Allow TCP connections upon SYN only" function has been activated and –The firewall rules have been adjusted or –If the function is activated (even without changing the firewall rules) After changing the firewall rules, the mGuard behaves in the same way as after a restart. However, this only applies to the forwarded connections. Existing TCP connections are interrupted, even if they are allowed according to the new firewall rules. Connections to the device are not affected, even if the firewall rules have been changed for remote access. When the function is not activated, the connections remain, even if the firewall rules changed would not allow them or would abort them. |
|
|
FTP |
If an outgoing connection is established to call data for the FTP protocol, two methods of data transmission can be used: With “active FTP”, the called server establishes an additional counter-connection to the caller in order to transmit data over this connection. With “passive FTP”, the client establishes this additional connection to the server for data transmission. FTP must be activated (default) so that additional connections can pass through the firewall. |
|
IRC |
Similar to FTP: for IRC chat over the Internet to work properly, incoming connections must be allowed following active connection establishment. IRC must be activated (default) in order for these connections to pass through the firewall. |
|
Default: deactivated Must be activated if VPN connections are to be established using PPTP from local computers to external computers without the aid of the mGuard . Must be activated if GRE packets are to be forwarded from the internal area to the external area. |
|
|
H.323 |
Default: deactivated Protocol used to establish communication sessions between two or more devices. Used for audio-visual transmission. This protocol is older than SIP. |
|
SIP |
Default: deactivated SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) is used to establish communication sessions between two or more devices. Often used in IP telephony. When the function is activated, it is possible for the mGuard to track the SIP and add any necessary firewall rules dynamically if further communication channels are established to the same session. When NAT is also activated, one or more locally connected computers can communicate with external computers by SIP via the mGuard . |
8.2Network Security >> Deep Packet Inspection
The Modbus protocol is often used to integrate automation devices in industrial applications. It enables process data to be exchanged between Modbus controllers regardless of the network structure. Modbus is a client/server protocol.
The TCP/IP version of the protocol is used to transmit data in industrial Ethernet: Modbus TCP. Access to specific device data is controlled via the Modbus TCP protocol using function codes.
Reserved TCP port 502 is usually used for transmission via the Modbus TCP protocol.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI)
The mGuard can inspect packets of incoming and outgoing Modbus TCP connections (Deep Packet Inspection) and filter them if required. The user data of incoming packets is inspected. Responses to filtered requests are not subject to further DPI.
Packets which use specific function codes can be “dropped” or “accepted” via defined rules.
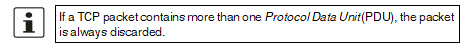
The following tab page appears when you click
on the  Edit Row icon:
Edit Row icon:

Network Security >> Deep Packet Inspection >> Modbus TCP >> Rule Records >> Edit |
||
|---|---|---|
Modbus TCP rule set |
Modbus TCP rule sets can only be used when a suitable license key is installed (Modbus TCP Inspector). The rules for filtering Modbus TCP packets are configured in rule records. These rule sets can be used in the following firewall tables if “TCP” is selected as the protocol: general packet filter / DMZ / GRE / IPsec VPN / OpenVPN client / PPP. 

|
|
Options |
Name |
A descriptive name |
Filter Rules |
Function code |
1 - 255 / Name of the function code / any Function codes in Modbus TCP connections indicate the purpose of data transmission, i.e., which operation is to be performed by the server (slave) based on the request from the client (master). You can select the function code from the drop-down list or enter it directly in the input field. |
|
PDU addresses (Only displayed for certain function codes) |
0 - 65535 / any Various addresses can be assigned to certain function codes (as PDU addresses based on 0). This setting can either be an individual PDU address (e.g., 47015) or an address area (e.g., 47010:47020). The PDU address area for incoming packets can either be partially or fully in the specified address area for the filter rule. 
|
|
Action |
Accept means that the data packets may pass through. Drop means that the data packets are not permitted to pass through. They are discarded, rendering the TCP connection unusable. It therefore cannot be used for further data transmission. A new TCP connection must be established for subsequent Modbus requests. If multiple rules are defined, these are queried starting from the top of the list of entries until an appropriate rule is found. This rule is then applied. If the list of rules contains further subsequent rules that could also apply, these rules are ignored. If no rule applies, the packet is discarded. |
|
Comment |
Freely selectable comment for this rule. |
|
Log |
For each individual Modbus TCP filter, you can specify whether the use of the rule: –Should be logged – activate Log action –Should not be logged – deactivate Log action (default) |
|
Log entries for unknown packets |
When the function is activated, the packets that are not covered by any of the created filter rules are logged. |
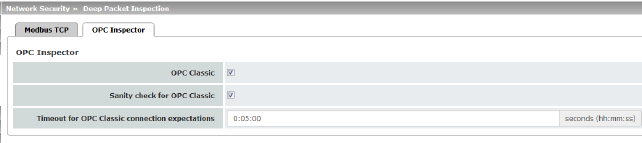
Network Security >> Deep Packet Inspection >> OPC Inspector |
||
|---|---|---|
OPC Inspector |
This function can only be activated when a suitable license key (OPC Inspector) is installed. With OPC Classic, communication always starts via TCP port 135. The client and server then negotiate one or more additional connections on new ports. To enable these connections, in the past all ports of an interconnected firewall had to be open. If OPC Classic is activated, it is enough to only enable TCP port 135 for a client/server pair using the firewall rules. The mGuard inspects the user data of the packets (Deep Packet Inspection). It checks in the user data sent via this port whether a new connection has been negotiated, and opens the negotiated port. To do so, communication between the client and the server on port 135 must be enabled in both directions. If OPC Classic is activated, NAT procedures can be used. If masquerading is to be used, port forwarding of port 135 to the OPC server/client must be activated on the LAN interface of the mGuard . |
|
|
If Sanity check for OPC Classic is activated, only OPC packets may be transmitted via OPC Classic port 135 (TCP) and the newly negotiated ports. |
|
|
Configures the timeout (in seconds) during which OPC traffic is expected. An existing OPC connection may negotiate another connection on a new port. If "Sanity check for OPC Classic" is activated, these connections must only be OPC connections. The mGuard creates a new dynamic firewall rule if it detects in OPC traffic that a new OPC connection should be established. The dynamic firewall rule immediately accepts new OPC connections with the negotiated parameters. If the timeout for the dynamic firewall expires, the rule is deleted. New connections with these parameters are then no longer accepted. Already established connections are not closed. |
|
8.3Network Security >> DoS Protection
This menu is not available on the FL MGUARD RS2000 , TC MGUARD RS2000 3G , TC MGUARD RS2000 4G , and FL MGUARD RS2005 . |
NOTE: Firewall setting affects DoS protection The DoS protection of the device is not available, if in the menu Network Security >> Packet Filter >> Incoming Rules "Accept all connections" is selected as the General firewall setting (see "Incoming Rules" on page 261). To provide DoS protection in this case, select the General firewall setting "Use the firewall ruleset below" and then create a firewall rule that accepts all connections. |
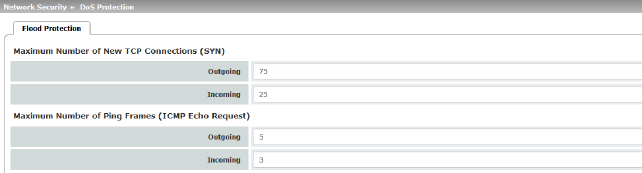
Network Security >> DoS Protection >> Flood Protection |
||
|---|---|---|
Maximum number of new TCP connections (SYN) |
Incoming/Outgoing |
Outgoing: default setting: 75 Incoming: default setting: 25 Maximum values for the number of incoming and outgoing TCP connections allowed per second. They are set to a value that can never be reached during normal practical operation. However, they can be easily reached in the event of attacks, thus providing additional protection. If there are special requirements in your operating environment, these values can be increased. |
Incoming/Outgoing |
Outgoing: default setting: 5 Incoming: default setting: 3 Maximum values for the number of incoming and outgoing “ping” packets allowed per second. They are set to a value that can never be reached during normal practical operation. However, they can be easily reached in the event of attacks, thus providing additional protection. If there are special requirements in your operating environment, these values can be increased. The value 0 means that no “ping” packets are allowed through or in. |
|
Maximum number of ARP requests or ARP replies each (Only in "Stealth" network mode) |
Incoming/Outgoing |
Default setting: 500 Maximum values for the number of incoming and outgoing ARP requests or replies allowed per second. They are set to a value that can never be reached during normal practical operation. However, they can be easily reached in the event of attacks, thus providing additional protection. If there are special requirements in your operating environment, these values can be increased. |
8.4Network Security >> User Firewall
This menu is not available on the FL MGUARD RS2000 , TC MGUARD RS2000 3G , TC MGUARD RS2000 4G , and FL MGUARD RS2005 . |
The user firewall is used exclusively by firewall users, i.e., users who are registered as firewall users (see "Authentication >> Firewall Users" on page 237).
Each firewall user can be assigned a set of firewall rules, also referred to as a template.
If a user firewall template or a firewall rule of a template is added, changed, deleted or disabled, this immediately affects all firewall users who are logged in.
Existing connections are interrupted. One exception is changing user firewall rules if the function "Abort existing connections upon firewall reconfiguration" is deactivated under Network Security >> Packet Filter >> Advanced . In this case, a network connection that exists due to a previously permitted rule is not interrupted.
If a firewall ruleset (template) is disabled, affected logged in firewall users still appear as logged in. However, the firewall rules from the disabled template no longer apply to them. If a firewall ruleset (template) is disabled and then enabled again, affected logged in firewall users must first log out and then log in again to reactivate the firewall rules from the template for themselves. |
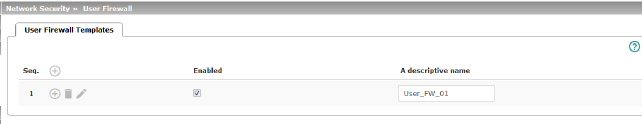
All defined user firewall templates are listed here. A template can consist of several firewall rules. A template can be assigned to several users.
Defining a new template:
•In the template table,
click on the  Insert
Row icon to add a new table row.
Insert
Row icon to add a new table row.
•Click on the  Edit Row icon.
Edit Row icon.
Editing a template:
•Click on the  Edit Row icon in the relevant row.
Edit Row icon in the relevant row.
Network Security >> User Firewall >> User Firewall Templates |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Enabled |
Activates/deactivates the relevant template. |
|
A descriptive name |
The name of the template. The name is specified when the template is created. |
The
following tab page appears when you click on the |
||
|
||
Options |
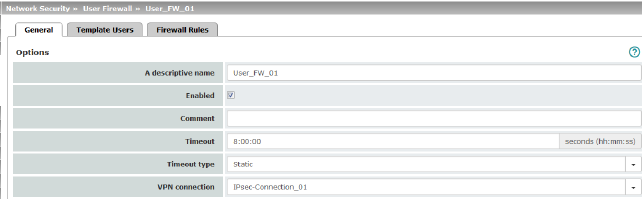
The user firewall template can be freely named/renamed. |
|
|
Enabled |
When the function is activated, the user firewall template becomes active as soon as firewall users log into the mGuard who are listed on the Template Users tab page (see below) and who have been assigned this template. It does not matter from which computer and under what IP address the user logs in. The assignment of the firewall rules to a user is based on the authentication data that the user enters during login (user name, password). |
|
Comment |
Optional explanatory text. |
|
Timeout |
Default: 8 hours (8:00:00) Specifies the time at which point the firewall rules are deactivated. If the user session lasts longer than the timeout time specified here, the user has to log in again. The entry can be in seconds [ss], minutes and seconds [mm:ss] or hours, minutes, and seconds [hh:mm:ss]. |
|
Static / Dynamic With a static timeout, users are logged out automatically as soon as the set timeout time has elapsed. With dynamic timeout, users are logged out automatically after all the connections have been closed by the user or have expired on the mGuard , and the set timeout time has subsequently elapsed. An mGuard connection is considered to have expired if no more data is sent for this connection over the following periods. |
|
|
Connection expiration period after non-usage: –TCP: 5 days (this value can be set, see "Timeout for established TCP connections" on page 280). 120 seconds are added after closing the connection. (These 120 seconds also apply to connections closed by the user.) –UDP: 30 seconds after data traffic in one direction; 180 seconds after data traffic in both directions –ICMP: 30 seconds –Others: 10 minutes |
|
|
VPN connection |
Specifies the VPN connection for which this user firewall rule is valid. This requires existing remote access through the VPN tunnel to the web interface. |
Network Security >> User Firewall >> User Firewall Templates >> Edit > ... |
||
|---|---|---|
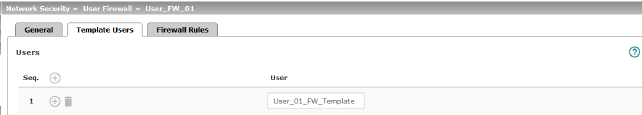
Specify the names of the users here. The names must correspond to those that have been defined under the Authentication >> Firewall Users menu (see Page 237). |
||
|
||
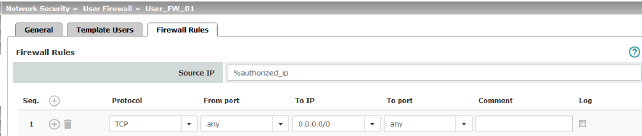
Firewall rules for the user firewall templates. When the template is configured with dynamic timeout approved UDPs and other network packets (excluding ICMP), reset the dynamic timeout to the initial value. |
||
|
||
|
IP address from which connections are allowed to be established. If this should be the address from which the user logged into the mGuard , the placeholder “%authorized_ip” should be used. 
|
|
|
Protocol |
All means TCP, UDP, ICMP, GRE, and other IP protocols. |
|
From port / To port (Only for TCP and UDP protocols) |
any refers to any port. startport:endport (e.g., 110:120) > port range. Individual ports can be specified using the port number or the corresponding service name (e.g., 110 for pop3 or pop3 for 110). Name of port groups, if defined. When a name is specified for a port group, the ports or port ranges saved under this name are taken into consideration (see "IP/Port Groups" on page 276). |
|
To IP |
0.0.0.0/0 means all IP addresses. To specify an address area, use CIDR format (see "CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing)" on page 29). Name of IP groups, if defined. When a name is specified for an IP group, the host names, IP addresses, IP areas or networks saved under this name are taken into consideration (see "IP/Port Groups" on page 276). 
|
|
Comment |
Freely selectable comment for this rule. |
|
Log |
For each firewall rule, you can specify whether the use of the rule: –Should be logged – activate Log function –Should not be logged – deactivate Log function (default) |
1 TC MGUARD RS4000/RS2000 3G , TC MGUARD RS4000/RS2000 4G , FL MGUARD RS4004/RS2005 , FL MGUARD RS4000/RS2000 , mGuard Centerport (Innominate) , FL MGUARD CENTERPORT , FL MGUARD RS , FL MGUARD BLADE , mGuard delta (Innominate)