
CIFS Integrity Monitoring is not available on the FL MGUARD RS2000 , TC MGUARD RS2000 3G , TC MGUARD RS2000 4G , and FL MGUARD RS2005 .
It must not be used on the FL MGUARD BLADE controller.
9CIFS Integrity Monitoring menu
CIFS Integrity Monitoring is not available on the FL MGUARD RS2000 , TC MGUARD RS2000 3G , TC MGUARD RS2000 4G , and FL MGUARD RS2005 . It must not be used on the FL MGUARD BLADE controller. |
In Stealth network mode, CIFS integrity checking is not possible without a management IP address. |
The CIFS-Anti-Virus-Scan-Connector function is no longer supported from mGuard firmware version 8.5. |
CIFS Integrity Checking
When CIFS Integrity Checking is performed, the Windows network drives are checked to determine whether certain files (e.g., *.exe, *.dll) have been changed. Changes to these files indicate a possible virus or unauthorized intervention.
Setting options for CIFS Integrity Checking
–Which network drives are known to the mGuard (see "CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> Importable Shares" on page 296).
–What type of access is permitted (see "CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> CIFS Integrity Checking >> Settings" on page 299).
–At what intervals the drives should be checked (see "CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> CIFS Integrity Checking >> Settings >> Edit >> Checked Share" on page 301).
–Which file types should be checked (see "CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> CIFS Integrity Checking >> Filename Patterns >> Edit" on page 308).
Warning method when a change is detected (e.g., via e-mail, see "CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> CIFS Integrity Checking >> Settings" on page 299 or via SNMP, see "CIFS Integrity Traps" on page 104).
9.1CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> Importable Shares
Requirements
The network drives that the mGuard should check regularly can be specified here.
In order for the network drives to be checked, you must also refer to these network drives in the CIFS Integrity Check. |
You can set the reference to the network drive for the CIFS integrity check, see "Checked CIFS share" on page 300.
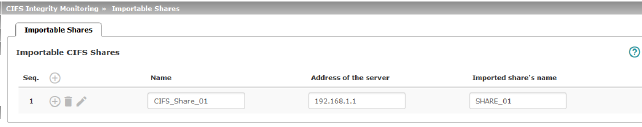
Importable CIFS Shares |
Name |
Name of the network drive to be checked (Internal name used in the configuration). |
IP address or DNS host name of the authorizing server. |
||
Name of the imported network drive |
Share name of the network drive that is to be checked. Click on the |
|
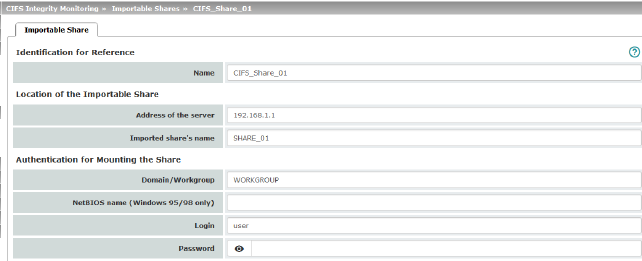
Identification for Reference |
Name |
Name of the network drive to be checked (Internal name used in the configuration). |
Location of the Importable Share |
Address of the server |
IP address or DNS host name of the authorizing server. |
|
Imported share's name |
Share name of the network drive that is to be checked. |
Authentication for Mounting the Share |
Name of the workgroup to which the network drive belongs. |
|
NetBIOS name (Windows 95/98 only) |
NetBIOS name for Windows 95/98 computers. |
|
Login |
Login (user identifier) for the server. |
|
Password |
Password for login. |
|
9.2CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> CIFS Integrity Checking
When CIFS Integrity Checking is performed, the Windows network drives are checked to determine whether certain files (e.g., *.exe, *.dll) have been changed. Changes to these files indicate a possible virus or unauthorized intervention.
Integrity database
If a network drive that is to be checked is reconfigured, an integrity database must be created.
This integrity database is used as the basis for comparison when checking the network drive regularly. The checksums of all files to be monitored are recorded here. The integrity database is protected against manipulation.
The integrity database is either created explicitly due to a specific reason (see CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> CIFS Integrity Checking >> Settings >> Edit >> Management , Actions ) or on the first regular check of the drive.
The integrity database must be created again following intentional manipulation of the relevant files of the network drive. Unauthorized manipulation of the relevant files cannot be detected if there is no (valid) integrity database. |
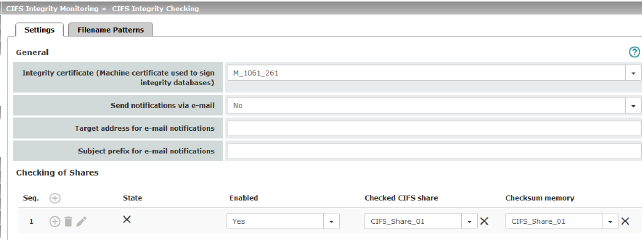
CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> CIFS Integrity Checking >> Settings |
||
|---|---|---|
General |
Integrity certificate (machine certificate used to sign integrity databases) |
Used to sign and check the integrity database so that it cannot be replaced or manipulated by an intruder without being detected. For information about certificates, please refer to "Machine Certificates" on page 246. |
|
Send notifications via e-mail |
After every check: an e-mail is sent to the address specified below after every check. No: an e-mail is not sent to the address specified below. Just in case of a failure or difference: an e-mail is sent to the address specified below if a deviation is detected during CIFS Integrity Checking or if the check could not be carried out due to an access error. |
|
Target address for e-mail notifications |
An e-mail is sent to this address either after every check or only if a deviation is detected during CIFS Integrity Checking or if the check could not be carried out due to an access error. |
|
Subject prefix for e-mail notifications |
Text entered in the subject field of the e-mail. |
|
(If network drives are defined) |
State of the network drive: –The network drive has not yet been checked. Probably no integrity database. –Last check finished successfully. –The process failed due to an unforeseen condition. Please consult the logs. –Last check was aborted due to timeout. –The integrity database is missing or incomplete. –The signature of the integrity database is invalid. –The integrity database was created with a different hash algorithm. –The integrity database is the wrong version. –The share which is to be checked is not available. –The share which is to be used as checksum memory is not available. –A file could not be read due to an I/O failure. Please consult the report. –The directory tree could not be traversed due to an I/O failure. Please consult the report. –All files in the share can be accessed successfully. An integrity check is possible. |
|
|
Enabled |
Yes: a check is triggered regularly for this network drive. No: a check is not triggered for this network drive. The mGuard has not connected this drive. The status cannot be viewed. Suspended: the check has been suspended until further notice. The status can be viewed. |
|
Name of the network drive to be checked (specified under CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> Importable Shares >> Edit ). |
|
|
Checksum memory |
In order to perform the check, the mGuard must be provided with a network drive for storing the files. The checksum memory can be accessed via the external network interface. |
Action |
Click on the |
|
Settings >> Checking of Shares >> Edit >> Checked Share
(see below)
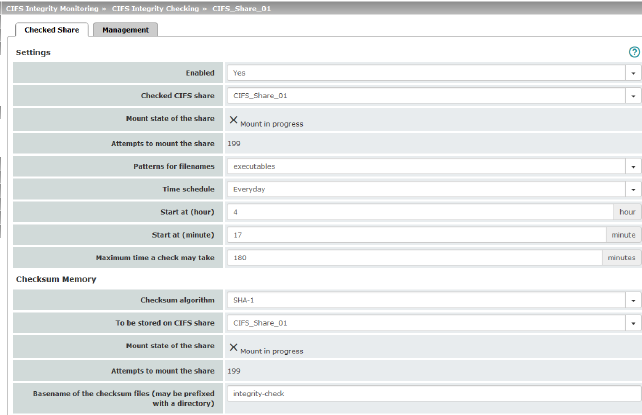
CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> CIFS Integrity Checking >> Settings >> Edit >> Checked Share |
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
Settings
|
Enabled |
Yes: a check is triggered regularly for this network drive. No: a check is not triggered for this network drive. The mGuard has not connected this drive. The status cannot be viewed. Suspended: the check has been suspended until further notice. The status can be viewed. |
|
Checked CIFS share |
Name of the network drive to be checked (specified under CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> Importable Shares >> Edit ). |
|
Mount state of the share |
Shows the mount state of the network drive. |
|
Attempts to mount the share |
Number of failed attempts to mount the network drive since its last reconfiguration or after restarting the mGuard . |
|
Patterns for filenames |
Specific file types are checked (e.g., only executable files such as *.exe and *.dll). The rules can be defined under CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> CIFS Integrity Checking >> Filename Patterns >> Edit . 

|
|
Time schedule |
Every Sunday, Every Monday, Every Tuesday, ... , Everyday, Several times a day, Continuous You can start the check every day, several times a day or on a specific weekday. 


The check can also be started manually (see CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> CIFS Integrity Checking >> Settings >> Edit >> Management , Actions ). |
|
Start at (hour) |
Time at which the check starts (hour). If “Several times a day” is selected, every 1 h, 2 h, 3 h, 4 h, 6 h, 8 h, 12 h |
|
Start at (minute) |
Time at which the check starts (minute). If “Several times a day” is selected, every 1 h, 2 h, 3 h, 4 h, 6 h, 8 h, 12 h |
|
Maximum time a check may take |
Maximum duration of the check sequence in minutes. You can therefore ensure that the check is completed in good time (e.g., before a shift starts). |
Checksum memory |
Checksum Algorithm |
MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256 (Default) Checksum algorithms such as MD5, SHA-1 or SHA-256 are used to check whether a file has been changed. SHA-256 is more secure than SHA-1, but it takes longer to process. The use of MD5 and SHA-1 is no longer recommended for security reasons (see "Using secure encryption and hash algorithms" on page 19). |
|
To be stored on CIFS share |
In order to perform the check, the mGuard must be provided with a network drive for storing the files. The checksum memory can be accessed via the external network interface. The same network drive can be used as the checksum memory for several different drives to be checked. The base name of the checksum files must then be clearly selected in this case. The mGuard recognizes which version the checksum files on the network drive must have. For example, if it is necessary to restore the contents of the network drive from a backup following a malfunction, old checksum files are provided in this case and the mGuard would detect the deviations. In this case, the integrity database must be recreated (see CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> CIFS Integrity Checking >> Settings >> Edit >> Management , Actions ). |
|
Mount state of the share |
Shows the mount state of the network drive. |
|
Attempts to mount the share |
Number of attempts to mount the network drive since its last reconfiguration or after restarting the mGuard . |
|
Basename of the checksum files (may be prefixed with a directory) |
The checksum files are stored on the network drive specified above. They can also be stored in a separate directory. The directory name must not start with a backslash (\). Example: Checksumdirectory\integrity-checksum “Checksumdirectory” is the directory and contains the files beginning with “integrity-checksum”. |
Settings >> Checking of Shares >> Edit >> Management
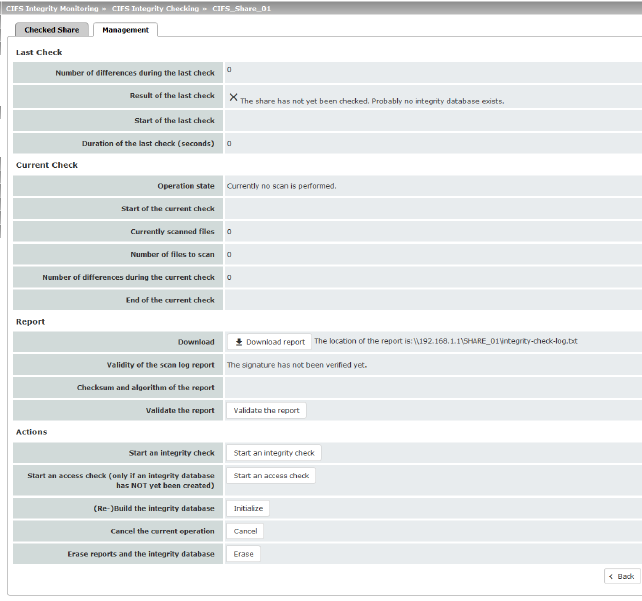
CIFS Integrity Monitoring >> CIFS Integrity Checking >> Settings >> Edit >> Management |
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
Last Check (Results are only displayed if a check has been carried out.) |
Number of differences during the last check |
Number of differences detected on the network drive. |
|
Result of the last check |
The result of the last check (see "State" on page 300). |
|
Start of the last check |
Weekday, month, day, HH:MM:SS (UTC). The local time may differ from this time. Example: the standard time in Germany is Central European Time (CET), which is UTC plus one hour. Central European Summer Time applies in summer, which is UTC plus two hours. |
|
Duration of the last check (seconds) |
Duration of the check in seconds. |
Current Check (Results are only displayed if a check has been carried out.)
|
Operation state |
Current operating state during the check: –Currently no scan is performed. –Scanning of this share is suspended. –Currently the share is being checked. –Currently an integrity database is being created. –Currently access permissions are checked. |
|
Start of the current check |
Starting point of the current integrity check. |
|
Currently scanned files |
Number of files scanned during the current check. |
|
Number of files to scan |
Total number of files to scan. |
|
Number of differences during the current check |
Number of differences detected on the network drive. |
|
End of the current check |
Estimated completion time for the check. |
Download |
The report is displayed here. It can be downloaded by clicking on the “Download report” button. The report is stored on the checked network drive as a log file with the file name “integrity-check-log.txt”. On every check, the results of the new check are added to the log file. When the file size reaches 32 MB, the file is renamed “integrity-check-log.txt.1” (backup file). A new log file (“integrity-check-log.txt”) containing the results of the current check is created. When this file reaches 32 MB, it is likewise renamed “integrity-check-log.txt.1” and the existing “integrity-check-log.txt.1” file is irrevocably overwritten. The integrity of the log files is ensured by creating checksums. Click on the “Validate the report” button to check whether the report is unchanged from the definition in the mGuard (according to the signature and certificate). |
|
|
Validity of the scan log report |
Result of the signature check: –The signature has not been verified yet. –The signature is valid. –ERROR: The report is missing. –ERROR: The report does not belong to this device or is not up to date. –ERROR: The report was created with a different checksum algorithm. –ERROR: The report was tampered with. –ERROR: The test report is not available. Check whether the network drive is connected (mounted). |
|
Checksum and algorithm of the report |
Checksum and algorithm |
|
Validate the report |
The signature for the report is checked. |
Start an integrity check |
Click on the Start an integrity check button to start the integrity check. The result of the check can be viewed in the report by clicking on the Download report button. 
|
|
|
Start an access check (only if an integrity database has NOT yet been created) |

Click on the Start an access check button to check whether there are files present on the imported network drive that the mGuard cannot access. More comprehensive creation of the integrity database is therefore not aborted in the absence of the proper access permissions. 
The result of the check can be viewed in the report by clicking on the Download report button. |
|
(Re-)Build the integrity database |

The mGuard creates a database with checksums in order to check whether files have been changed. A change to executable files indicates a virus. However, if these files have been changed intentionally, a new database must be created by clicking on the Initialize button in order to prevent false alarms. The creation of an integrity database is also recommended if network drives have been newly set up. Otherwise, an integrity database is set up during the first scheduled check instead of a check being performed (if an access check was not performed first). |
|
Cancel the current procedure |
Click on the Cancel button to stop the integrity check. |
|
Erase reports and the integrity database |
Click on the Erase button to delete all existing reports/databases. A new integrity database must be created for any further integrity checks. This can be initiated by clicking on the Initialize button. Otherwise, a new integrity database is created automatically on the next scheduled check (if an access check was not performed first). This procedure cannot be seen. |
