Logging refers to the recording of event messages, e.g., regarding settings that have been made, the application of firewall rules, errors, etc.
Log entries are recorded in various categories and can be sorted and displayed according to these categories (see “Logging >> Browse Local Logs” on page 328).

All log entries are recorded in the RAM of the mGuard by default. Once the maximum memory space for log entries has been used up, the oldest log entries are automatically overwritten by new entries. In addition, all log entries are deleted when the mGuard is switched off.
To prevent this, log entries can be transmitted to an external computer (remote server). This is particularly useful if you wish to manage the logs of multiple mGuard devices centrally.
Remote Logging |
The log entries can be transferred to an external log server (syslog server) using the remote logging function. To check on the external log server whether log entries are transmitted regularly, an "UPTIME" log entry is created approximately every 30 minutes and sent to the syslog server. The log entry shows the current uptime of the mGuard device. Example: 2024-12-25_08:20:00.90770 uptime-audit: -------- UPTIME: 29 min -------- |
|
|
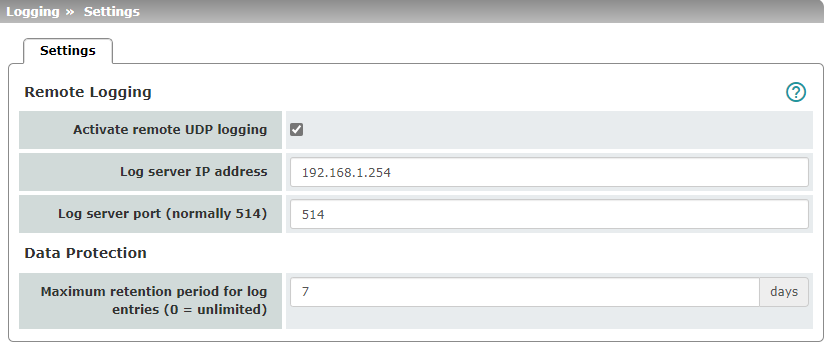
Activate remote UDP logging |
If you want all log entries to be transmitted to the external log server (specified below), activate the function.
|
|
Log server IP address |
Specify the IP address of the log server to which the log entries should be transmitted via UDP. An IP address must be specified, not a host name. This function does not support name resolution because it might not be possible to make log entries if a DNS server fails. |
|
Log server port |
Specify the port of the log server to which the log entries should be transmitted via UDP. Default: 514 |
|

|
|
|
–If the “IPsec VPN >> Connections >> Edit >> General”, Local option is set to 1:1 NAT (see page 266), the following applies: The internal IP address must be located in the specified local network. –If the “IPsec VPN >> Connections >> Edit >> General”, Remote option is set to 1:1 NAT (see page 268), the following applies: The IP address of the remote log server must be located in the network that is specified as Remote in the definition of the VPN connection. |
|
Data Protection |
Log entries may contain personal data. In order to comply with basic data protection requirements, it is possible to store log entries on the device only for a limited period of time. After a configurable retention period has expired, log entries are automatically deleted from the device.
|
|
|
Maximum retention period for log entries (0 = unlimited) |
Default: 0 (no limit) Specifies the maximum number of days after which a locally stored log entry is deleted on the device. The value 0 (default setting) means that there is no maximum retention period for the deletion of log entries. 

Maximum retention period: 365 days |
11.2Logging >> Browse Local Logs
mGuard devices have different functions depending on the model. Depending on the available functions, the log entries can be filtered by category so that only the intended log entries are visible in the WBM.
To display one or more categories, enable the check boxes for the desired categories. The log entries are continuously updated according to the selection.
To pause or continue the continuous updating
of the log entries, click on the  Pause or
Pause or  Continue button.
Continue button.
Access to log entries
The log entries can be accessed in various ways
mGuard |
UDP |
Web interface (web UI) |
|---|---|---|
/var/log/dhclient |
No |
Common |
/var/log/dhcp-ext |
No |
DHCP Server/Relay |
/var/log/dhcp-int |
No |
DHCP Server/Relay |
/var/log/dhcp-dmz |
No |
DHCP Server/Relay |
/var/log/dnscache |
No |
No |
/var/log/dynrouting |
socklog |
Dynamic Routing |
/var/log/firestarter |
svlogd |
IPsec VPN |
/var/log/firewall |
svlogd |
Network Security |
/var/log/fwrulesetd |
socklog |
Network Security |
/var/log/https |
No |
No |
/var/log/ipsec |
socklog |
IPsec VPN |
/var/log/l2tp |
No |
IPsec VPN |
/var/log/lldpd |
No |
SNMP/LLDP |
/var/log/maid |
No |
Common |
/var/log/main |
socklog |
Common |
/var/log/maitrigger |
No |
No |
/var/log/openvpn |
socklog |
OpenVPN Client |
/var/log/pluto |
svlogd |
IPsec VPN |
/var/log/psm-sanitize |
No |
Common |
/var/log/pullconfig |
socklog |
Common |
/var/log/redundancy |
socklog |
Common |
/var/log/snmp |
No |
SNMP/LLDP |
/var/log/tinydns |
No |
Common |
/var/log/userfwd |
socklog |
Network Security |
.
Logging >> Browse Local Logs >> Categories |
||
|---|---|---|
General |
Log entries that cannot be assigned to other categories. Examples (without time stamp): HTTPS (Login/Logout) –Webinterface: Failed login for '*******' role '*******' from 192.168.1.55 by Web –Webinterface: Accepted login for 'user1' role 'admin' from 192.168.1.55 by Web –Webinterface: Logout for 'user1' role 'admin' from 192.168.1.55 by timeout SSH (Login) –sshd[28296]: Accepted password for admin from 192.168.1.55 port 49248 ssh2 –inno-sshlimitd: accepting new connection at fd 6 –inno-sshlimitd: allow session 1 of maximum 4 for role admin (class 1) at fd 6 –ssh[28472]: session start for user 'admin' Action –maid[12138]: User 'user1' performed a configuration change with role 'admin': –maid[12138]: NTP_ENABLE set to 'no' |
|
Network Security / Firewall |
Logged events are shown here if the logging of events was selected when defining the firewall rules (Log = enabled). Log ID and number for tracing errors Log entries that relate to the firewall rules listed below have a log ID and number. This log ID and number can be used to trace the firewall rule to which the corresponding log entry relates and that led to the corresponding event. Firewall rules and their log ID –Packet filters: “Network Security >> Packet Filter >> Incoming Rules” menu “Network Security >> Packet Filter >> Outgoing Rules” menu Log ID: fw-incoming or fw-outgoing –Firewall rules for VPN connections: “IPsec VPN >> Connections >> Edit >> Firewall” menu, Incoming/Outgoing Log ID: fw-vpn-in or fw-vpn-out –Firewall rules for OpenVPN connections: “OpenVPN Client >> Connections >> Edit >> Firewall” menu, Incoming/Outgoing Log ID: fw-openvpn-in or fw-openvpn-out “OpenVPN Client >> Connections >> Edit >> NAT” menu Log ID: fw-openvpn-portfw |
|
|
–Firewall rules for web access to the mGuard via HTTPS: “Management >> Web Settings >> Access” menu Log ID: fw-https-access |
|
|
–Firewall rules for access to the mGuard via SNMP: “Management >> SNMP >> Query” menu Log ID: fw-snmp-access –Firewall rules for SSH remote access to the mGuard: “Management >> System Settings >> Shell Access” menu Log ID: fw-ssh-access –Firewall rules for access to the mGuard via NTP: “Management >> System Settings >> Time and Date” menu Log ID: fw-ntp-access |
|
|
–Firewall rules for the user firewall: “Network Security >> User Firewall” menu, Firewall Rules Log ID: ufw- –Rules for NAT, port forwarding: “Network >> NAT >> IP and Port Forwarding” menu Log ID: fw-portforwarding |
|
|
Searching for firewall rules based on a network security log As of mGuard firmware version 8.6.0, firewall log entries in the list are highlighted in blue and provided with a hyperlink. A click on the firewall log entry, e. g. fw-https-access-1-1ec2c133-dca1-1231-bfa5-000cbe01010a opens the configuration page (menu >> submenu >> tab) with the firewall rule that caused the log entry. |
|
IPsec VPN |
Lists all VPN events. The format corresponds to standard Linux format. There are special evaluation programs that present information from the logged data in a more easily readable format. |
|
OpenVPN |
Lists all OpenVPN events. |
|
DHCP Server/Relay |
Messages fraom the services that can be configured under “Network >> DHCP”.
|
|
SNMP/LLDP |
Messages from the services that can be configured under “Management >> SNMP”. |
|