
This menu is not available on the FL MGUARD RS2000, TC MGUARD RS2000 3G, TC MGUARD RS2000 4G, and FL MGUARD RS2005.
|
This menu is not available on the FL MGUARD RS2000, TC MGUARD RS2000 3G, TC MGUARD RS2000 4G, and FL MGUARD RS2005. |
QoS (Quality of Service) refers to the quality of individual transmission channels in IP networks. This relates to the allocation of specific resources to specific services or communication types so that they work correctly. For example, the necessary bandwidth must be provided to transmit audio or video data in real time in order to reach a satisfactory communication level. At the same time, slower data transfer by FTP or e-mail does not threaten the overall success of the transmission process (file or e-mail transfer).
An ingress filter prevents the processing of certain data packets by filtering and dropping them before they enter the mGuard processing mechanism. The mGuard can use an ingress filter to avoid processing data packets that are not needed in the network. This results in faster processing of the remaining, i.e., required data packets.
Using suitable filter rules, administrative access to the mGuard can be ensured with high probability, for example.
Packet processing on the mGuard is generally defined by the handling of individual data packets. This means that the processing performance depends on the number of packets to be processed and not on the bandwidth.
Filtering is performed exclusively according to features that are present or may be present in each data packet: the sender and receiver IP address specified in the header, the specified Ethernet protocol, the specified IP protocol, the specified TOS/DSCP value, and/or the VLAN ID (if VLANs have been set up). As a check must be carried out to see if the filter rules apply to each individual data packet, the list of filter rules should be kept as short as possible. Otherwise, the time spent on filtering could be longer than the time actually saved by setting the filter.
Please note that not all specified filter criteria should be combined. For example, it does not make sense to specify an additional IP protocol in the same rule set that contains the ARP Ethernet protocol. Nor does it make sense to specify a sender or receiver IP address if the IPX Ethernet protocol is specified (in hexadecimal format).

Internal: settings for ingress filters at the LAN interface
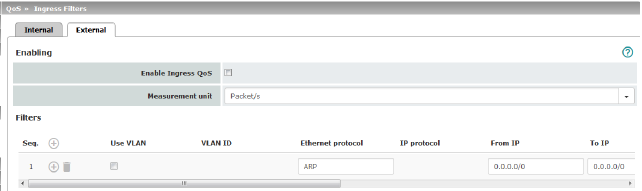
External: settings for ingress filters at the WAN interface
|
Enabling |
Enable Ingress QoS |
Deactivated (default): this feature is disabled. If filter rules are defined, they are ignored. Activated: this feature is enabled. Data packets may only pass through and be forwarded to the mGuard for further evaluation and processing if they comply with the filter rules defined below. Filters can be set for the LAN port (Internal tab) and the WAN port (External tab). |
|
|
Measurement unit |
kbit/s / Packet/s Specifies the unit of measurement for the numerical values entered further down under Guaranteed and Upper limit. |
|
Filter |
Use VLAN |
If a VLAN is set up, the relevant VLAN ID can be specified to allow the relevant data packets to pass through. 
|
|
|
VLAN ID (When Use VLAN is activated) |
Specifies that the VLAN data packets that have this VLAN ID may pass through. |
|
|
Ethernet protocol |
Specifies that only data packets of the specified Ethernet protocol may pass through. Possible entries: ARP, IPV4, %any. Other entries must be in hexadecimal format (up to 4 digits). (The ID of the relevant protocol in the Ethernet header is entered here. It can be found in the publication of the relevant standard.) |
|
|
IP protocol |
All / TCP / UDP / ICMP / ESP Specifies that only data packets of the selected IP protocol may pass through. When set to All, no filtering is applied according to the IP protocol. |
|
|
From IP |
Specifies that only data packets from the specified IP address may pass through. 0.0.0.0/0 stands for all addresses, i.e., in this case no filtering is applied according to the IP address of the sender. To specify an address area, use CIDR format (see “CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing)” on page 29). |
|
|
To IP |
Specifies that only data packets that should be forwarded to the specified IP address may pass through. Entries correspond to From IP, as described above. 0.0.0.0/0 stands for all addresses, i.e., in this case no filtering is applied according to the IP address of the sender. |
|
|
Current TOS/DSCP |
Each data packet contains a TOS or DSCP field. (TOS stands for Type of Service, DSCP stands for Differentiated Services Code Point.) The traffic type to which the data packet belongs is specified here. For example, an IP phone will write a different entry in this field for outgoing data packets compared to an FTP program. When a value is selected here, only data packets with this value in the TOS or DSCP field may pass through. When set to All, no filtering according to the TOS/DSCP value is applied. |
|
|
Guaranteed |
The number entered specifies how many data packets per second or kbps can pass through at all times – according to the option set under Measurement unit (see above). This applies to the data stream that conforms to the rule set criteria specified on the left (i.e., that may pass through). The mGuard may drop the excess number of data packets in the event of capacity bottlenecks if this data stream delivers more data packets per second than specified. |
|
|
Upper limit |
The number entered specifies the maximum number of data packets per second or kbps that can pass through – according to the option set under Measurement unit (see above). This applies to the data stream that conforms to the rule set criteria specified on the left (i.e., that may pass through). The mGuard drops the excess number of data packets if this data stream delivers more data packets per second than specified. |
|
|
Comment |
Optional comment text. |
The services are assigned corresponding priority levels. In the event of connection bottlenecks, the outgoing data packets are placed in egress queues (i.e., queues for pending packets) according to the assigned priority level and are then processed according to their priority. Ideally, the assignment of priority levels and bandwidths should result in a sufficient bandwidth level always being available for the real-time transmission of data packets, while other packets, e.g., FTP downloads, are temporarily set to wait in critical cases.
The main application of egress QoS is the optimal utilization of the available bandwidth on a connection. In certain cases, it may be useful to limit the packet rate, e.g., to protect a slow computer from overloading in the protected network.
The Egress Queues function can be used for all interfaces. Up to mGuard firmware version 8.6.x, the function can also be used for VPN connections. In firmware version 8.7.0 the use of QoS in VPN connections is no longer possible.
13.2.1Internal/External/External 2/Dial-in
Internal: settings for egress queues at the LAN interface
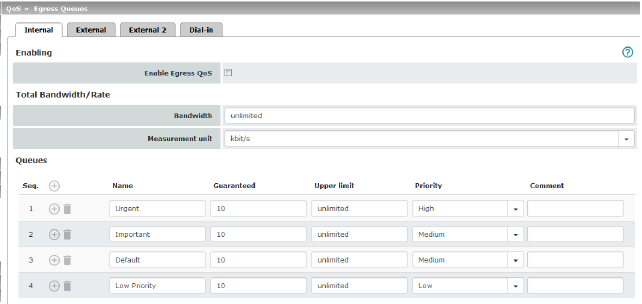
External/External 2/Dial-in:
The tabs for egress queues at the WAN interface (External), the secondary external interface (External 2), and for packets for PPP dial-up connection (Dial-in) feature the same setting options as the tabs for the LAN interface (Internal).
In all cases, the settings relate to the data that is sent externally into the network from the relevant mGuard interface.
|
QoS menu >> Egress Queues >> Internal/External/External 2/Dial-in |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Enabling |
Deactivated (default): this feature is disabled. Activated: this feature is enabled. This option is recommended if the interface is connected to a network with low bandwidth. This enables bandwidth allocation to be influenced in favor of particularly important data. |
|
|
Total Bandwidth/Rate |
Total maximum bandwidth that is physically available – specified in kbps or packets per second (see below: Measurement unit). In order to optimize prioritization, the total bandwidth specified here should be slightly lower than the actual amount. This prevents a buffer overrun on the transferring devices, which would result in adverse effects. |
|
|
|
Measurement unit |
kbit/s / Packet/s Specifies the unit of measurement for the numerical values (see above: Bandwidth). |
|
Queues |
Name |
The default name for the egress queue can be adopted or another can be assigned. The name does not specify the priority level. |
|
|
Guaranteed |
Bandwidth that should be available at all times for the relevant queue. Based on the selection under Measurement unit (kbit/s or Packet/s), meaning that the unit of measurement does not have to be specified explicitly here. The total of all guaranteed bandwidths must be less than or equal to the total bandwidth. |
|
|
Upper limit |
Maximum bandwidth available that may be set for the relevant queue by the system. Based on the selection under Measurement unit (kbit/s or Packet/s), meaning that the unit of measurement does not have to be specified explicitly here. The value must be greater than or equal to the guaranteed bandwidth. The value unlimited can also be specified, which means that there is no further restriction. |
|
|
Priority |
Low / Medium / High Specifies with which priority the relevant queue, if available, should be processed, provided the total available bandwidth has not been exhausted. |
|
|
Comment |
Optional comment text. |
|
The Egress Queues (VPN) function is no longer available in mGuard firmware version 8.7.0. An update to mGuard firmware version 8.7.0 from an older firmware version with activated Egress Queues (VPN) function is not possible. |
This page defines the rules for the data that is assigned to the defined egress queues (see above) in order for the data to be transmitted with the priority assigned to the relevant queue.
Rules can be defined separately for all interfaces and for VPN connections.
13.4.1Internal/External/External 2/Dial-in
Internal: settings for egress queue rules
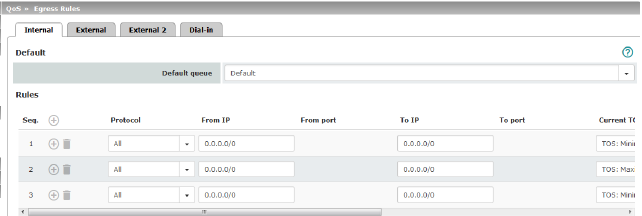
External/External 2/Dial-in:
The tabs for egress queue rules at the WAN interface (External), the secondary external interface (External 2), and for packets for PPP dial-up connection (Dial-in) feature the same setting options as the tabs for the LAN interface (Internal).
In all cases, the settings relate to the data that is sent externally into the network from the relevant mGuard interface.
|
QoS >> Egress Rules >> Internal/External/External 2/Dial-in |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Default |
Default queue |
Name of the egress queue (user-defined). The names of the queues are displayed as listed or specified under Egress Queues on the Internal/External/VPN via External tabs. The following default names are defined: Default/Urgent/Important/Low Priority. Traffic that is not assigned to a specific egress queue under Rules remains in the default queue. You can specify which egress queue should be used as the default queue in this selection list. |
|
Rules |
The assignment of specific data traffic to an egress queue is based on a list of criteria. If the criteria in a row apply to a data packet, it is assigned to the egress queue specified in the row. Example: for audio data to be transmitted, you have defined a queue with guaranteed bandwidth and priority under Egress Queues (see page 390) under the name Urgent. You then define the rules here for how audio data is detected and specify that this data should belong to the Urgent queue. |
|
|
|
Protocol |
All / TCP / UDP / ICMP / ESP Protocol(s) relating to the rule. |
|
|
IP address of the network or device from which the data originates. 0.0.0.0/0 means all IP addresses. To specify an address area, use CIDR format (see “CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing)” on page 29). Assign the traffic from this source to the queue selected under Queue name in this row. |
|
|
|
From port (Only for TCP and UDP protocols) |
Port used at the source from which the data originates. any refers to any port. startport:endport (e.g., 110:120) refers to a port range. Individual ports can be specified using the port number or the corresponding service name (e.g., 110 for pop3 or pop3 for 110). |
|
|
To IP |
IP address of the network or device to which the data is sent. Entries correspond to From IP, as described above. |
|
|
To port (Only for TCP and UDP protocols) |
Port used at the source where the data is sent. Entries correspond to From port, as described above. |
|
|
Current TOS/DSCP |
Each data packet contains a TOS or DSCP field. (TOS stands for Type of Service, DSCP stands for Differentiated Services Code Point.) The traffic type to which the data packet belongs is specified here. For example, an IP phone will write a different entry in this field for outgoing data packets compared to an FTP program that uploads data packets to a server. When a value is selected here, only data packets that have this value in the TOS or DSCP field are chosen. These values are then set to a different value according to the entry in the New TOS/DSCP field. |
|
|
New TOS/DSCP |
If you want to change the TOS/DSCP values of the data packets that are selected using the defined rules, enter the text that should be written in the TOS/DSCP field here. For a more detailed explanation of the Current TOS/DSCP and New TOS/DSCP options, please refer to the following RFC documents: – RFC 3260 “New Terminology and Clarifications for Diffserv” – RFC 3168 “The Addition of Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) to IP” – RFC 2474 “Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field)” – RFC 1349 “Type of Service in the Internet Protocol Suite” |
|
|
Name of the egress queue to which traffic should be assigned. |
|
|
|
Comment |
Optional comment text. |
|
The Egress Rules (VPN) function is no longer available in mGuard firmware version 8.7.0. An update to mGuard firmware version 8.7.0 from an older firmware version with activated Egress Rules (VPN) function is not possible. |